LIVE
SILTATION |
 |
1. CATEGORY
1.0 – River Training
2. DESIGN STATUS
Level II
3. ALSO KNOWN AS
Vertical brush layering
4. DESCRIPTION
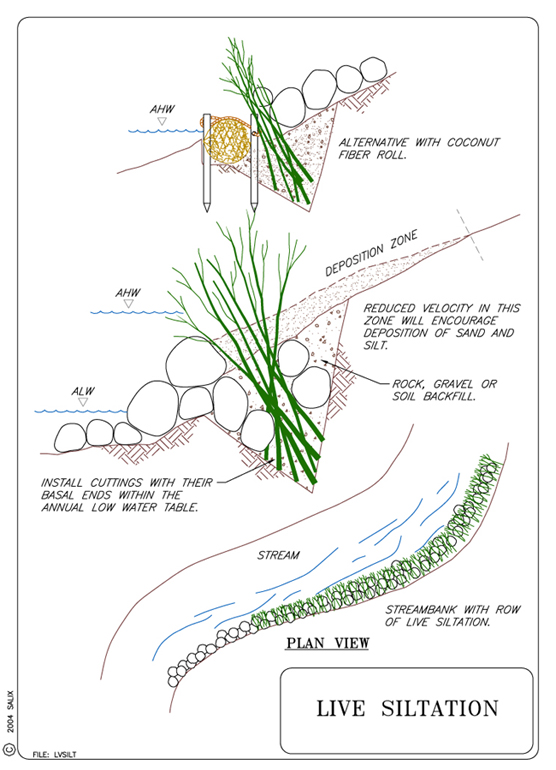
Live siltation is a revegetation technique used to secure the toe of a streambank, trap sediments, and create fish rearing habitat. The system can be constructed as a living or a non-living brushy system at the water’s edge.
5. PURPOSE
Live siltation helps to secure the toe of a streambank, and trap sediments.
6. PLANNING
Useful for Erosion Processes:
Toe erosion with upper bank failure Scour of middle and upper banks by currents
Local scour Erosion of local lenses or layers of noncohesive sediment
Erosion by overbank runoff General bed degradation
Headcutting
Piping
Erosion by navigation waves
Erosion by wind waves
Erosion by ice and debris gouging General bank instability or susceptibility to mass slope failure
Spatial Application:
Instream Toe Midbank Top of Bank
Hydrologic / Geomorphic Setting
Resistive Redirective Continuous Discontinuous Outer Bend Inner Bend Incision Lateral Migration Aggradation Conditions Where Practice Applies:
Live siltation is an appropriate practice along an outer bend with sufficient scour or toe protection.
Complexity:
Low.
7. ENVIRONMENTAL CONSIDERATIONS / BENEFITS
This is a very effective and simple conservation method using local plant materials. This technique is particularly valuable for providing immediate cover and fish habitat while other revegetation plantings become established. The protruding branches provide roughness, slow velocities, and encourage deposition of sediment. The depositional areas are then available for natural recruitment of native riparian vegetation.
8. HYDRAULIC LOADING
This technique may be used for velocities up to 2 m/sec (6.6 ft/sec), but velocities should be at least 0.25 m/sec (0.8 ft/sec) for the system to function properly.
9. COMBINATION OPPORTUNITIES
Live siltation techniques can be constructed in combination with rock toes, Rootwad Revetments, Coconut Fiber Rolls, Live Fascines, and Brush Mattresses.
10. ADVANTAGES
This is a very effective and simple conservation method using local plant materials. This technique is particularly valuable for providing immediate cover and fish habitat while other revegetation plantings become established. The protruding branches provide roughness, slow velocities, and encourage deposition of sediment. The depositional areas are then available for natural recruitment of native riparian vegetation.
11. LIMITATIONS
If using a living system, cuttings must be taken during the dormancy period.
12. MATERIALS AND EQUIPMENT
Natural stone, willow wattles, logs or root wad revetments are needed for toe and scour protection. The live siltation will require live branches of shrub willows 1-1.5 m (3.5–5 ft) in length. The branches should be dormant, and need to have the side branches still attached. Any woody plant material, such as alder, can be installed for a non-living system.
13. CONSTRUCTION / INSTALLATION
Construct a V-shaped trench at the annual high water (AHW) level, with hand tools or a backhoe. Excavate a trench so that it parallels the toe of the streambank and is approximately 0.6 m (2 ft) deep. Lay a thick layer of willow branches in the trench so that 1/3 of the length of the branches is above the trench and the branches angle out toward the stream. Place a minimum of 40 willow branches per m (12 branches per ft) in the trench.
Backfill over the branches with a gravel/soil mix and secure the top surface with large washed gravel, bundles/coir logs, or carefully placed rocks. Both the upstream and downstream ends of the live siltation construction need to transition smoothly into a stable streambank to reduce the potential for the system to wash out. More that one row of live siltation can be installed. A living and growing siltation system typically is installed at AHW. A non-living system can be constructed below AHW during low water levels. If it is impossible to dig a trench, the branches can be secured in place with logs, armor rock, bundles made from wattles, or coir logs.
14. COST
0.7-2 work hours per linear m (0.2-0.6 work hours per linear ft), plus willow stock if not readily available on site.
15. MAINTENANCE / MONITORING
During the first year, the installation should be checked for failures after all 1-year return interval and higher flows, and repaired as necessary. During summer months of the first year, ensure that cuttings are not becoming dehydrated.
16. COMMON REASONS / CIRCUMSTANCES FOR FAILURE
Cuttings will not promote siltation as well if not located at the water’s edge. If located further up the bank, cuttings may dry out, and will only trap sediments and slow velocities during high flows. Cuttings may not grow well if not handled properly prior to installation. See Special Topic: Harvesting and Handling of Woody Cuttings for proper handling instructions.
17. CASE STUDIES AND EXAMPLES
The following pictures are of Live Siltation used in conjunction with Turf Reinforcement Mats on Alamitos Creek in Santa Clara County, CA. The Live Siltation was installed in October 2003.
At another site on the same creek, a few hundred feet away from the previous site, Modified Live Siltation was installed along with the TRM and Live Siltation.
Please visit the Photo Gallery for more pictures.
18. RESEARCH OPPORTUNITIES
Research into velocities that this technique can withstand would be helpful.
19. REFERENCES
McCullah, J. A. (2004). Bio Draw 3.0. Salix Applied Earthcare, Redding, CA